| Children can talk or through actions show: | |
| H1 | how to make informed decisions about health |
| H2 | about the elements of a balanced, healthy lifestyle |
| H3 | about choices that support a healthy lifestyle, and recognise what might influence these |
| H4 | how to recognise that habits can have both positive and negative effects on a healthy lifestyle |
| H5 | about what good physical health means; how to recognise early signs of physical illness |
| H6 | about what constitutes a healthy diet; how to plan healthy meals; benefits to health and wellbeing of eating nutritionally rich foods; risks associated with not eating a healthy diet including obesity and tooth decay. |
| H7 | how regular (daily/weekly) exercise benefits mental and physical health (e.g. walking or cycling to school, daily active mile); recognise opportunities to be physically active and some of the risks associated with an inactive lifestyle |
| H8 | about how sleep contributes to a healthy lifestyle; routines that support good quality sleep; the effects of lack of sleep on the body, feelings, behaviour and ability to learn |
| H9 | that bacteria and viruses can affect health; how everyday hygiene routines can limit the spread of infection; the wider importance of personal hygiene and how to maintain it |
| H10 | how medicines, when used responsibly, contribute to health; that some diseases can be prevented by vaccinations and immunisations; how allergies can be managed |
| H11 | how to maintain good oral hygiene (including correct brushing and flossing); why regular visits to the dentist are essential; the impact of lifestyle choices on dental care (e.g. sugar consumption/acidic drinks such as fruit juices, smoothies and fruit teas; the effects of smoking) |
| H12 | about the benefits of sun exposure and risks of overexposure; how to keep safe from sun damage and sun/heat stroke and reduce the risk of skin cancer. |
| H13 | about the benefits of the internet; the importance of balancing time online with other activities; strategies for managing time online |
| H14 | how and when to seek support, including which adults to speak to in and outside school, if they are worried about their health |
| H15 | that mental health, just like physical health, is part of daily life; the importance of taking care of mental health |
| H16 | about strategies and behaviours that support mental health — including how good quality sleep, physical exercise/time outdoors, being involved in community groups, doing things for others, clubs, and activities, hobbies and spending time with family and friends can support mental health and wellbeing |
| H17 | to recognise that feelings can change over time and range in intensity |
| H18 | about everyday things that affect feelings and the importance of expressing feelings |
| H19 | a varied vocabulary to use when talking about feelings; about how to express feelings in different ways |
| H20 | strategies to respond to feelings, including intense or conflicting feelings; how to manage and respond to feelings appropriately and proportionately in different situations |
| H21 | to recognise warning signs about mental health and wellbeing and how to seek support for themselves and others |
| H22 | to recognise that anyone can experience mental ill health; that most difficulties can be resolved with help and support; and that it is important to discuss feelings with a trusted adult |
| H23 | about change and loss, including death, and how these can affect feelings; ways of expressing and managing grief and bereavement |
| H24 | problem-solving strategies for dealing with emotions, challenges and change, including the transition to new schools |
| H25 | about personal identity; what contributes to who we are (e.g. ethnicity, family, gender, faith, culture, hobbies, likes/dislikes) |
| H26 | that for some people gender identity does not correspond with their biological sex |
| H27 | to recognise their individuality and personal qualities |
| H28 | to identify personal strengths, skills, achievements and interests and how these contribute to a sense of self-worth |
| H29 | about how to manage setbacks/perceived failures, including how to re-frame unhelpful thinking |
| H30 | to identify the external genitalia and internal reproductive organs in males and females and how the process of puberty relates to human reproduction |
| H31 | to identify the external genitalia and internal reproductive organs in males and females and how the process of puberty relates to human reproduction |
| H32 | about how hygiene routines change during the time of puberty, the importance of keeping clean and how to maintain personal hygiene |
| H33 | about the processes of reproduction and birth as part of the human life cycle; how babies are conceived and born (and that there are ways to prevent a baby being made); how babies need to be cared for¹ |
| H34 | about where to get more information, help and advice about growing and changing, especially about puberty |
| H35 | about the new opportunities and responsibilities that increasing independence may bring |
| H36 | strategies to manage transitions between classes and key stages |
| H37 | reasons for following and complying with regulations and restrictions (including age restrictions); how they promote personal safety and wellbeing with reference to social media, television programmes, films, games and online gaming. |
LKS2 – PSHE
YEAR 3/4 (LKS2) - Examples of 'Expected' in the core skill of - Health and Wellbeing, Relationships, Living in the Wider World
Health and Wellbeing - Core Skills
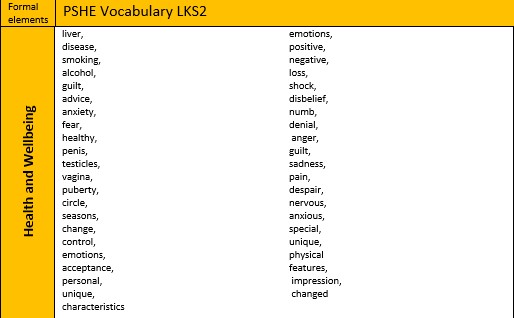
Health and Wellbeing - Vocabulary
Relationships - Core Skills
| Children can talk or through actions show: | |
| R1 | to recognise that there are different types of relationships (e.g. friendships, family relationships, romantic relationships, online relationships) |
| R2 | that people may be attracted to someone emotionally, romantically and sexually; that people may be attracted to someone of the same sex or different sex to them; that gender identity and sexual orientation are different |
| R3 | about marriage and civil partnership as a legal declaration of commitment made by two adults who love and care for each other, which is intended to be lifelong |
| R4 | that forcing anyone to marry against their will is a crime; that help and support is available to people who are worried about this for themselves or others |
| R5 | that people who love and care for each other can be in a committed relationship (e.g. marriage), living together, but may also live apart |
| R6 | that a feature of positive family life is caring relationships; about the different ways in which people care for one another |
| R7 | to recognise and respect that there are different types of family structure (including single parents, same-sex parents, step-parents, blended families, foster parents); that families of all types can give family members love, security and stability |
| R8 | to recognise other shared characteristics of healthy family life, including commitment, care, spending time together; being there for each other in times of difficulty |
| R9 | how to recognise if family relationships are making them feel unhappy or unsafe, and how to seek help or advice |
| R10 | about the importance of friendships; strategies for building positive friendships; how positive friendships support wellbeing |
| R11 | what constitutes a positive healthy friendship (e.g. mutual respect, trust, truthfulness, loyalty, kindness, generosity, sharing interests and experiences, support with problems and difficulties); that the same principles apply to online friendships as to face-to-face relationships |
| R12 | to recognise what it means to ‘know someone online’ and how this differs from knowing someone face-to-face; risks of communicating online with others not known face-to-face |
| R13 | the importance of seeking support if feeling lonely or excluded |
| R14 | strategies for recognising and managing peer influence and a desire for peer approval in friendships; to recognise the effect of online actions on others |
| R15 | how friendships can change over time, about making new friends and the benefits of having different types of friends |
| R16 | that friendships have ups and downs; strategies to resolve disputes and reconcile differences positively and safely |
| R17 | to recognise if a friendship (online or offline) is making them feel unsafe or uncomfortable; how to manage this and ask for support if necessary |
| R18 | about the impact of bullying, including offline and online, and the consequences of hurtful behaviour |
| R19 | strategies to respond to hurtful behaviour experienced or witnessed, offline and online (including teasing, name-calling, bullying, trolling, harassment or the deliberate excluding of others); how to report concerns and get support |
| R20 | about discrimination: what it means and how to challenge it |
| R21 | about privacy and personal boundaries; what is appropriate in friendships and wider relationships (including online); |
| R22 | about why someone may behave differently online, including pretending to be someone they are not; strategies for recognising risks, harmful content and contact; how to report concerns |
| R23 | how to respond safely and appropriately to adults they may encounter (in all contexts including online) whom they do not know |
| R24 | recognise different types of physical contact; what is acceptable and unacceptable; strategies to respond to unwanted physical contact |
| R25 | about seeking and giving permission (consent) in different situations |
| R26 | about keeping something confidential or secret, when this should (e.g. a birthday surprise that others will find out about) or should not be agreed to, and when it is right to break a confidence or share a secret |
| R27 | how to recognise pressure from others to do something unsafe or that makes them feel uncomfortable and strategies for managing this |
| R28 | where to get advice and report concerns if worried about their own or someone else’s personal safety (including online) |
| R29 | about how to manage setbacks/perceived failures, including how to re-frame unhelpful thinking |
| R30 | that personal behaviour can affect other people; to recognise and model respectful behaviour online |
| R31 | to recognise the importance of self-respect and how this can affect their thoughts and feelings about themselves; that everyone, including them, should expect to be treated politely and with respect by others (including when online and/or anonymous) in school and in wider society; strategies to improve or support courteous, respectful relationships |
| R32 | about respecting the differences and similarities between people and recognising what they have in common with others e.g. physically, in personality or background |
| R33 | to listen and respond respectfully to a wide range of people, including those whose traditions, beliefs and lifestyle are different to their own |
| R34 | how to discuss and debate topical issues, respect other people’s point of view and constructively challenge those they disagree with |
Relationships - Vocabulary
Living in the Wider World - Core Skills
| Children can talk or through actions show: | |
| L1 | to recognise reasons for rules and laws; consequences of not adhering to rules and laws |
| L2 | to recognise there are human rights, that are there to protect everyone |
| L3 | about the relationship between rights and responsibilities |
| L4 | the importance of having compassion towards others; shared responsibilities we all have for caring for other people and living things; how to show care and concern for others |
| L5 | ways of carrying out shared responsibilities for protecting the environment in school and at home; how everyday choices can affect the environment (e.g. reducing, reusing, recycling; food choices) |
| L6 | about the different groups that make up their community; what living in a community means |
| L7 | to value the different contributions that people and groups make to the community |
| L8 | about diversity: what it means; the benefits of living in a diverse community; about valuing diversity within communities |
| L9 | about stereotypes; how they can negatively influence behaviours and attitudes towards others; strategies for challenging stereotypes |
| L10 | about prejudice; how to recognise behaviours/actions which discriminate against others; ways of responding to it if witnessed or experienced |
| L11 | to appreciate the range of national, regional, religious and ethnic identities in the United Kingdom |
| L12 | about some of the different ways information and data is shared and used online, including for commercial purposes |
| L13 | about how information on the internet is ranked, selected and targeted at specific individuals and groups; that connected devices can share information |
| L14 | recognise things appropriate to share and things that should not be shared on social media; rules surrounding distribution of images |
| L15 | about how text and images in the media and on social media can be manipulated or invented; strategies to evaluate the reliability of sources and identify misinformation |
| L16 | about the different ways to pay for things and the choices people have about this |
| L17 | to recognise that people have different attitudes towards saving and spending money; what influences people’s decisions; what makes something ‘good value for money’ |
| L18 | that people’s spending decisions can affect others and the environment (e.g. Fair trade, buying single-use plastics, or giving to charity) |
| L19 | to recognise that people make spending decisions based on priorities, needs and wants |
| L20 | different ways to keep track of money |
| L21 | about risks associated with money (e.g. money can be won, lost or stolen) and ways of keeping money safe |
| L22 | about the risks involved in gambling; different ways money can be won or lost through gambling-related activities and their impact on health, wellbeing and future aspirations |
| L23 | to identify the ways that money can impact on people’s feelings and emotions |
| L24 | to recognise positive things about themselves and their achievements; set goals to help achieve personal outcomes |
| L25 | that there is a broad range of different jobs/careers that people can have; that people often have more than one career/type of job during their life |
| L26 | about stereotypes in the workplace and that a person’s career aspirations should not be limited by them |
| L27 | about what might influence people’s decisions about a job or career (e.g. personal interests and values, family connections to certain trades or businesses, strengths and qualities, ways in which stereotypical assumptions can deter people from aspiring to certain jobs) |
| L28 | that some jobs are paid more than others and money is one factor which may influence a person’s job or career choice; that people may choose to do voluntary work which is unpaid |
| L29 | about some of the skills that will help them in their future careers e.g. teamwork, communication and negotiation |
| L30 | to identify the kind of job that they might like to do when they are older |
| L31 | to recognise a variety of routes into careers (e.g. college, apprenticeship, university) |
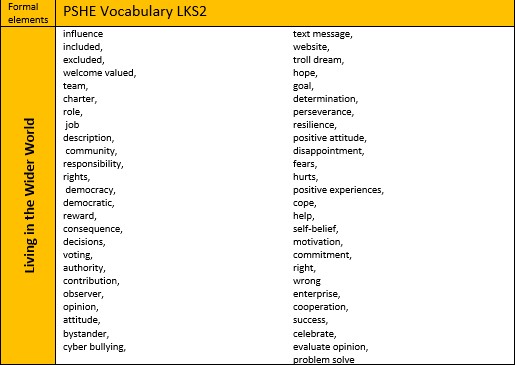
Living in the Wider World - Vocabulary